Ransomware attacks are continuing to rise in scale, cost, and sophistication. The effects can be detrimental by disrupting operations, exposing sensitive data, and leaving businesses with difficult recovery decisions. So, whether you’re managing a small business or a large enterprise, preparation is your strongest defence.
In this post, we will break down a practical, actionable and easy to follow checklist of the 10 most important steps you can take right now to strengthen your ransomware defences. From robust backups to incident response planning, this guide will help you assess your current security posture and close the gaps before an attack ever hits.
In the recent years, there has been a considerable rise in the amount of ransomware attacks. In their 2024 annual review, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) stated that ‘Ransomware attacks continue to pose the most immediate and disruptive threat to our critical national infrastructure (CNI)’, showing how important It is that we behave proactively to prevent ransomware attacks rather than sitting around and waiting for the threat to become real.
Specifically, a ransomware attack aims to block access to your data until a ransom has been paid. It is a type of malware attack that destroys or encrypts files and folders on a computer, server or device, to then attempt to extort money in exchange for a key to unlock the encrypted device. But even when paid, cybercriminals might never give the key to the business or device owner and stop their threats.

The impact caused by ransomware attacks can be tremendous. Operationally, this could cause a loss of access to data and downtime for you and your clients, consequently leading to delays and missed deadlines. It will also cost you financially, again due to downtime but also potential fines for lack of compliance and loss of customers who may feel you have acted unsafely with their data. We all know that there is a trust relationship built between business and client.
Ransomware attacks are a huge threat to organisations of all sizes; they are no longer rare, they’re routine. Whether you’re managing a small business network or an enterprise environment, having a clear checklist to minimise your exposure and maximise your response is essential.
Now lets get onto the checklist…
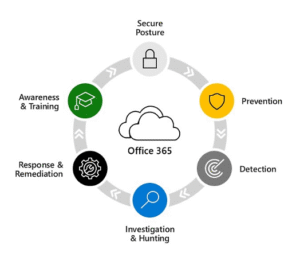
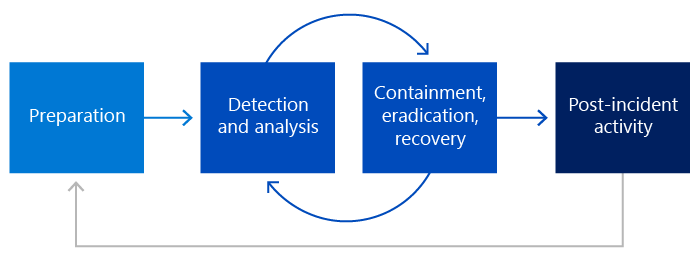
Ransomware isn’t a matter of if, but when. As attacks become more frequent and more damaging, having a clear, proactive defence strategy is essential, not optional. By following this checklist, you’re not just ticking boxes, you’re building a layered, resilient approach to cybersecurity that can significantly reduce your risk and minimise the impact of an attack.
Now is the time to evaluate your current defences, close the gaps, and ensure that your team knows exactly how to respond if the worst happens. Treat cybersecurity as an ongoing priority, not a one-time project.
Your readiness today could make all the difference tomorrow!
Important Links:
Go to our Buy page for more information: https://a4scloud.solutions/hardware-software-cloudassets/
You can find more information about Microsoft for Endpoint here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/defender-endpoint/microsoft-defender-endpoint
Read Microsoft’s Ransomware post here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/security/business/security-101/what-is-ransomware
Read our latest blog post here: https://a4scloud.solutions/microsoftcopilotaibusinessbenefits/
Read our latest LinkedIn post here: https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7330902690350133248
References:
2024 annual review, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)’
